
That line, scribbled on a whiteboard at VRM Day recently at the Computer History Museum, expresses the unspoken social contract we’ve always had with ad-supported print publications in the physical world. But we never needed to say it in that world, for the same reason we never needed to say “don’t follow me out of your store,” or “don’t use ink that will give me an infection.” Nobody ever would have considered doing anything that ridiculously ill-mannered.
But following us, and infecting our digital bodies (e.g. our browsers) with microbes that spy on us, is pro forma for ad-supported publishers on the Internet. That’s why Do Not Track was created in 2007, and a big reason why since then hundreds of millions of us have installed ad blockers and tracking protection of various kinds in our browsers and mobile devices.
But blocking ads also breaks that old social contract. In that sense it’s also ill-mannered (though not ridiculously so, given the ickyness that typifies so much advertising online).
What if we wanted to restore that social contract, for the good of publishers that are stuck in their own ill-mannered death spiral?
The first and easiest way is by running tracking protection alone. There are many ways of doing that. There are settings you can make in some browsers, plus add-ons or extensions from Aloodo, Baycloud, Disconnect, the EFF and others.
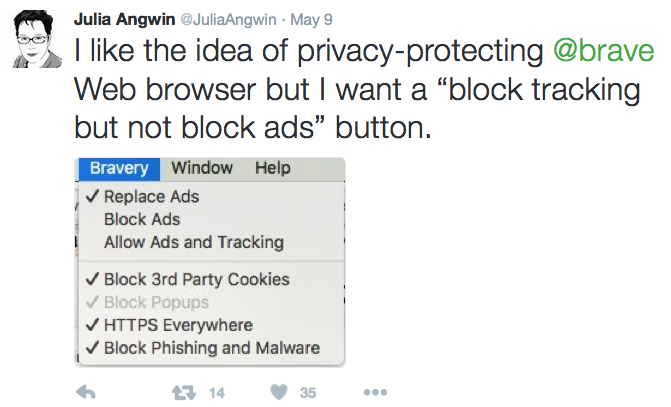
The second is requesting refined settings from browser makers. That’s what @JuliaAnguin does in this tweet about the new Brave browser:
But why depend on each browser to provide us with a separate setting, with different rules? How about having our own pro forma rule we could express through all our browsers and apps?
We have the answer, and it’s called the NoStalking rule. In fact, it’s already being worked out and formalized at the Kantara Initiative and will live at Customer Commons, where it will be legible at all three of these levels:
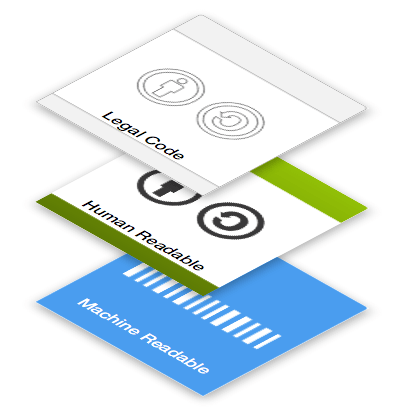
It will work because it’s a good one for both sides. Individuals proffering the #NoStalking term get guilt-free use of the goods they come to the publisher for, and the publisher gets to stay in business — and improve that business by running advertising that is actually valued by its recipients.
The offer can be expressed in one line of code in a browser, and accepted by corresponding code on the publisher’s side. The browser code can be run natively (as, for example, a choice in the Brave menu above) or through an extension such as an ad or tracking blocker. In those cases the blocker would open the valve to non-tracking-based advertising.
On the publisher’s side, the agreement can be automatic. Or simply de facto, meaning the publisher only runs non-tracking based ads anyway. (As does, for example, Medium.) In that case, the publisher is compliant with CHEDDAR, which was outlined by Don Marti (of Aloodo, above) and discussed both at VRM Day and then at IIW, in May. Here’s an icon-like image for CHEDDAR, drawn by Craig Burton on his phone:
To explain CHEDDAR, Don wrote this on the same whiteboard where the NoStalking term above also appeared:
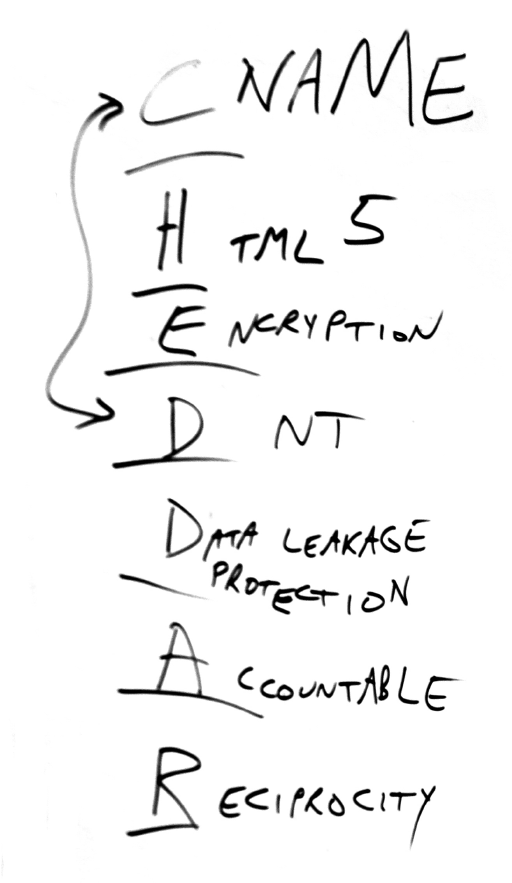
For the A in CHEDDAR, if we want the NoStalking agreement to be accountable from both sides, it might help to have a consent receipt. That spec is in the works too.
What matters most is that individuals get full respect as sovereign actors operating with full agency in the marketplace. That means it isn’t good enough just for sites to behave well. Sites also need to respond to friendly signals of intent coming directly from individuals visiting those sites. That’s why the NoProfiling agreement is important. It’s the first of many other possible signals as well.
It also matters that the NoProfiling agreement may be the first of its kind in the online world: one where the individual is the one extending the offer and the business is the one agreeing to it, rather than the other way around.
At VRM Day and IIW, we had participants affiliated with the EFF, Mozilla, Privacy Badger, Adblock Plus, Consent Receipt, PDEC (Personal Data Ecosystem Consortium), and the CISWG (Consent & InfoSharing Working Group), among others. Work has continued since then, and includes people from the publishing, advertising and other interested communities. There’s a lot to be encouraged about.
In case anybody wonders if advertising can work as well if it’s not based on tracking, check out Pedro Gardete: The Real Price of Cheap Talk: Do customers benefit from highly targeted online ads? by Eilene Zimmerman (@eilenez) in Insights by Stanford Business. The gist:
Now a new paper from Stanford Graduate School of Business professor Pedro Gardete and Yakov Bart, a professor at Northeastern University, sheds light on who is likely to benefit from personalized advertising and identifies managerial best practices.
The researchers found that highly targeted and personalized ads may not translate to higher profits for companies because consumers find those ads less persuasive. In fact, in some cases the most effective strategy is for consumers to keep information private and for businesses to track less of it.
You can also mine the oeuvres of Bob Hoffman and Don Marti for lots of other material that makes clear that the best advertising is actual advertising, and not stalking-based direct marketing that only looks like advertising.
Our next step, while we work on all this, is to put together an FAQ on why the #NoProfiling deal is a good one for everybody. Look for that at Customer Commons, where terms behind more good deals that customers offer will show up in the coming months.

0 Comments
2 Pingbacks