Experimental Covid-19 Vaccines Given to Hundreds of Thousands of Chinese

Hundreds of thousands of people have taken an experimental Covid-19 vaccine developed by China National Biotec Group (CNBG) in the past two months, including Chinese subjects not enrolled in clinical trials, CNBG said.
The final trials are still underway to prove that the vaccines are safe and effective, but China’s drug regulator authorized three experimental coronavirus vaccines for emergency use among those in high-risk groups such as medical workers, pandemic response officials, border inspection agents and members of the military.
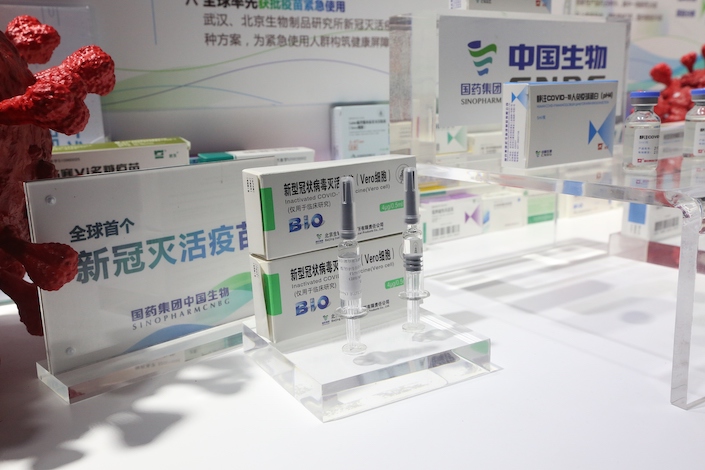
China officially launched the emergency-use program in July, but certain state-owned companies internally started having employees take the vaccine as early as June, workers told Caixin. CNBG, China’s leading coronavirus developer, said its vaccine has proven to be safe and to have good immunogenicity in various animal tests, and the product has obtained clinical study approval from China’s State Food and Drug Administration, according to an informed consent form for emergency vaccination viewed by Caixin.
Now emergency use of the vaccines is expanding. China’s civil aviation authorities recently provided vaccines for front-line workers at airlines and airports. Zheng Zhongwei, head of China’s coronavirus vaccine task force, said the government is considering expanding the emergency program to cover workers at produce markets, transport industry officials, and service workers.
A Covid-19 vaccine developed by Sinovac Biotech Ltd., a Nasdaq-listed Chinese vaccine developer, was also approved for emergency use. Sinovac Chairman and Chief Executive Officer Yin Weidong told Reuters that 90% of its employees—as many as 3,000 workers—and their families have been injected with the company’s vaccine candidate even though it hasn’t completed late-stage trials.
The hundreds of thousands of vaccine recipients can provide valuable data to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of vaccine candidates, but the data can’t be used as the basis for approval for commercial application, Yin said. He, his wife and parents have all received the vaccine, Yin said. Sinovac is conducting Phase III trials in Brazil and Indonesia.
CanSino Biologics, another Chinese vaccine developer included in the emergency program, said its vaccine has been used by some Chinese peacekeepers. The company didn’t disclose how many members of the military have taken the vaccine.
In an interview with Chinese state-owned television, Yu Xuefeng, chairman and CEO of CanSino Biologics, said commercial use must be supported by effective data from Phase III clinical trials.
China has been a leader in the race to develop Covid-19 vaccines, contributing five of the nine vaccines that have reached late-stage Phase III trials. About 135 vaccine candidates are under development worldwide. Among them, about 10% use a traditional approach employing a weakened or inactive form of the virus, as does the CNBG candidate.
Starting in June, more than 1,000 employees of a Beijing-based state-owned company voluntarily received the CNBG vaccine, an employee of the Beijing company told Caixin. The person said he got the shot after the employer called for volunteers several times. The company requires all expatriate workers to take the vaccine before they can leave China, the person said.
Several other companies, including state-owned and private companies such as Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd., have started providing vaccines to employees, mostly to expatriate workers, according to employees at the companies.
CNBG said its vaccine was developed by a Beijing-based unit. According to publicly announced vaccine development progress, the inoculation was still in early phases of clinical safety trials when it started to be put into use. On April 27, the vaccine was tested in Shangqiu, Henan province. On June 28, the company disclosed preliminary trial results showing that all participants produced antibodies against the Covid-19 virus within 28 days of receiving two doses of vaccine.
Even though Phase I/II clinical trials show that a vaccine induces neutralizing antibody responses, that isn’t enough to prove a vaccines is effective in protecting patients, experts said.
Another informed consent form for emergency vaccination viewed by Caixin emphasizes that due to differences among recipients’ immune systems, it cannot be ruled out that certain people may not obtain immune protection from the vaccine.
As with any other vaccine, the informed consent form listed common reactions that may occur after injection with the Covid-19 vaccine, including fever, headache, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, muscle pain, joint pain and lethargy. The employee of the state-owned company said recipients of the CNBG vaccine are required to report only fever.
CNBG said it signed agreements with Huawei and Phoenix Television, a partially state-owned television network, to provide resources and service support for routine and emergency vaccinations. CNBG is conducting Phase III trials abroad, including in the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, Peru, Morocco and Argentina.
Scientists said they aren’t sure how effectively these experimental vaccines can protect people from coronavirus infection.
“Since there’s no proven vaccine yet, any candidate that can help us in preventing and controlling the pandemic is necessary,” said Xiong Sidong, president of Soochow University and Director of the Institute of Biology and Medical Sciences.
The World Health Organization warned that widespread immunization against Covid-19 may not be in the cards until the middle of next year.
Contact reporter Denise Jia (huijuanjia@caixin.com) and editor Bob Simison (bobsimison@caixin.com)
Download our app to receive breaking news alerts and read the news on the go.

- PODCAST
- MOST POPULAR